Let’s learn how to implement Google Maps on iOS with Swift 3. We gonna install the SDK via CocoaPods, so you will not gonna miss how to learn to use latest version of CocoaPods. In addition we will also learn to use extra APIs from Google; Distance Matrix and Direction. Not to be forget to use URLSession.
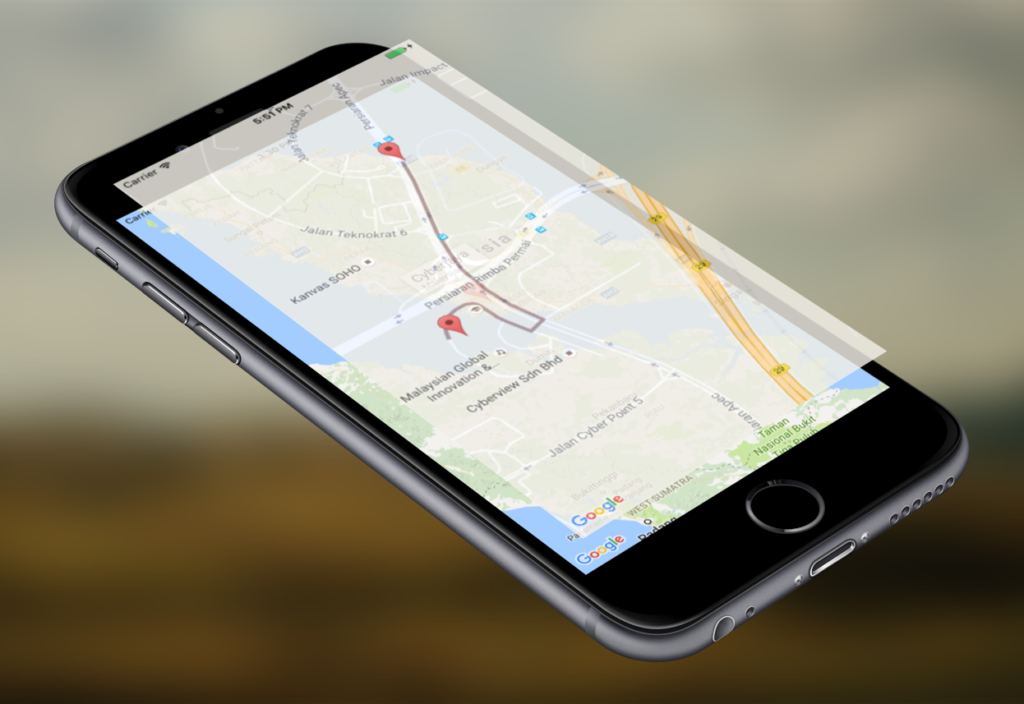
Displaying Google Maps on iOS App
1. Installing with CocoaPods.
Create a new iOS single view project. We will use a CocoaPods to install Google Maps SDK into the project.
target 'Google Maps App' do
pod 'GoogleMaps'
end
2. Get API Key
Go to the Google API Console to obtain API key. Use iOS-restricted API key so that you can use the key for multiple prototype projects. For production app, you need to make an independant key.
To create a API key, first you need to create a project. Then enable the Google Maps SDK for iOS.
Then go to ‘Credential’, click on ‘Click credentials’ > ‘API Key’. Just create what ever it’s prompt but you need to go back to edit the credential to rename it and make key restriction for ‘iOS apps’ with specified app id then hit ‘Save’.
3. Implement on the App
Open Info.plist add this key Privacy - Location When In Use Usage Description with appropriate description value.
At AppDelegate.swift add this codes:
import GoogleMaps
GMSServices.provideAPIKey("<#YOUR OWN API KEY>")
At ViewController.swift. Don’t forget to import GoogleMaps framework.
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Create a GMSCameraPosition that tells the map to display the
// coordinate 2.909960,101.654674 at zoom level 16.
let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withLatitude: 2.909960, longitude:101.654674, zoom: 16.0)
let mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: CGRect.zero, camera: camera)
mapView.isMyLocationEnabled = true
view = mapView
// Creates a marker in the center of the map.
let marker = GMSMarker()
marker.position = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 2.909960, longitude: 101.654674)
marker.title = "Cyberjaya"
marker.snippet = "Malaysia"
marker.map = mapView
let marker2 = GMSMarker()
marker2.position = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 2.915142, longitude: 101.657498)
marker2.title = "MSC"
marker2.snippet = "Malaysia"
marker2.map = mapView
}

It will show you two places, when you tap on the pin it will show a callout.
Get More Information from Google APIs
1. Enable more API
Go to Google API console, please enable ‘Google Maps Distance Matrix API‘ and ‘Google Maps Direction API‘.
Get Distance from Point A to Point B
Getting the information can be simply through GET call. Like this
let a_coordinate_string = "2.915142,101.657498"
let b_coordinate_string = "2.909960,101.654674"
let urlString = "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?units=metric&origins=\(a_coordinate_string)&destinations=\(b_coordinate_string)&key="<#YOUR-API-KEY>"
API Request with URLSession
Google Maps Distance Matrix API
Usually we will use 3rd library framework like Alamofire, which can be installed via CocoaPods but we probably want to use something more simpler, but using iOS library it self. We have something that is similar which called URLRequest.
Here is the snippet of how it works. Add this code after creating the maps code inside ‘viewDidLoad‘.
let a_coordinate_string = "2.915142,101.657498"
let b_coordinate_string = "2.909960,101.654674"
let urlString = "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?units=metric&origins=\(a_coordinate_string)&destinations=\(b_coordinate_string)&key=<#GOOGLE_API_KEY#>"
guard let url = URL(string: urlString) else {
print("Error: cannot create URL")
return
}
let urlRequest = URLRequest(url: url)
// set up the session
let config = URLSessionConfiguration.default
let session = URLSession(configuration: config)
// make the request
let task = session.dataTask(with: urlRequest, completionHandler: { (data, response, error) in
do {
guard let data = data else {
throw JSONError.NoData
}
guard let json = try JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: []) as? NSDictionary else {
throw JSONError.ConversionFailed
}
print(json)
} catch let error as JSONError {
print(error.rawValue)
} catch let error as NSError {
print(error.debugDescription)
}
})
task.resume()
Also add this JSONError Handler.
enum JSONError: String, Error {
case NoData = "ERROR: no data"
case ConversionFailed = "ERROR: conversion from JSON failed"
}
With this code you will request, from point A to point B which will return something like this.
{
"destination_addresses" = (
"Cyberjaya, 63000 Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia"
);
"origin_addresses" = (
"Persiaran Apec, Cyberjaya, 63000 Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia"
);
rows = (
{
elements = (
{
distance = {
text = "1.0 km";
value = 1044;
};
duration = {
text = "3 mins";
value = 163;
};
status = OK;
}
);
}
);
status = OK;
}
To retrive it using URLSession
if let array = json["routes"] as? NSArray {
if let routes = array[0] as? NSDictionary{
if let overview_polyline = routes["overview_polyline"] as? NSDictionary{
if let points = overview_polyline["points"] as? String{
print(points)
// Use DispatchQueue.main for main thread for handling UI
DispatchQueue.main.async {
// show polyline
let path = GMSPath(fromEncodedPath:points)
self.polyline.path = path
self.polyline.strokeWidth = 4
self.polyline.strokeColor = UIColor.init(hue: 210, saturation: 88, brightness: 84, alpha: 1)
self.polyline.map = self.mapView
}
}
}
}
}
Direction API
The Google Maps Directions API is a service that calculates directions between locations. You can search for directions for several modes of transportation, including transit, driving, walking, or cycling.
let a_coordinate_string = "2.915142,101.657498"
let b_coordinate_string = "2.909960,101.654674"
let urlString = "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/directions/json?origin=\(a_coordinate_string)&destination=\(b_coordinate_string)&key=<#YOUR_API_KEY#>"
For usage for Google Maps Direction API, go back to Google API console, go to the project’s credential make sure you restricted to IP address to your IP address to make sure the request is acceptable by Google.
You will get the return something like this.
{
"geocoded_waypoints" = (
{
"geocoder_status" = OK;
"place_id" = ChIJTSTvxAG3zTER1MSTU4SZygQ;
types = (
route
);
},
{
"geocoder_status" = OK;
"place_id" = ChIJU2JeJBu3zTERTePHnzNJs58;
types = (
political,
sublocality,
"sublocality_level_1"
);
}
);
routes = (
{
bounds = {
northeast = {
lat = "2.9151702";
lng = "101.6574231";
};
southwest = {
lat = "2.9092747";
lng = "101.6543312";
};
};
copyrights = "Map data \U00a92016 Google";
legs = (
{
distance = {
text = "1.0 km";
value = 1043;
};
duration = {
text = "3 mins";
value = 164;
};
"end_address" = "Cyberjaya, 63000 Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia";
"end_location" = {
lat = "2.910136";
lng = "101.6543312";
};
"start_address" = "Persiaran Apec, Cyberjaya, 63000 Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia";
"start_location" = {
lat = "2.9151702";
lng = "101.6574231";
};
steps = (
{
distance = {
text = "0.7 km";
value = 680;
};
duration = {
text = "1 min";
value = 87;
};
"end_location" = {
lat = "2.9093766";
lng = "101.656123";
};
"html_instructions" = "Head south on Persiaran Apec toward Jalan Teknokrat 6";
polyline = {
points = "yjxP{}mkRl@NXHVHb@NvBv@|B|@r@V^NNDbAVHBl@NdAVb@F`AFT?nABzBG\\CbBWZG";
};
"start_location" = {
lat = "2.9151702";
lng = "101.6574231";
};
"travel_mode" = DRIVING;
},
{
distance = {
text = "48 m";
value = 48;
};
duration = {
text = "1 min";
value = 14;
};
"end_location" = {
lat = "2.9092747";
lng = "101.6557006";
};
"html_instructions" = "Turn right";
maneuver = "turn-right";
polyline = {
points = "sfwPwumkRFXLx@";
};
"start_location" = {
lat = "2.9093766";
lng = "101.656123";
};
"travel_mode" = DRIVING;
},
{
distance = {
text = "0.3 km";
value = 315;
};
duration = {
text = "1 min";
value = 63;
};
"end_location" = {
lat = "2.910136";
lng = "101.6543312";
};
"html_instructions" = "Turn rightDestination will be on the left";
maneuver = "turn-right";
polyline = {
points = "}ewPcsmkRwBb@MBQ@S@M?M?]@Q?K?E@C?C@EDC@CDCFCJ?HAH?L@L@NBLBJFPFLFFHJHFFFRJf@R";
};
"start_location" = {
lat = "2.9092747";
lng = "101.6557006";
};
"travel_mode" = DRIVING;
}
);
"traffic_speed_entry" = (
);
"via_waypoint" = (
);
}
);
"overview_polyline" = {
points = "yjxP{}mkRbCr@hI|CjCp@hB^vAFnABzBG`C[ZGFXLx@wBb@_@Da@@iA@SHOZ?n@D\\J\\NTRRZRf@R";
};
summary = "Persiaran Apec";
warnings = (
);
"waypoint_order" = (
);
}
);
status = OK;
}
This is the snippet get the ‘overview_polyline’.
if let array = json["rows"] as? NSArray {
if let rows = array[0] as? NSDictionary{
if let array2 = rows["elements"] as? NSArray{
if let elements = array2[0] as? NSDictionary{
if let duration = elements["duration"] as? NSDictionary {
if let text = duration["text"] as? String{
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.lbl_eta_duration.text = text;
}
}
}
if let duration = elements["distance"] as? NSDictionary {
if let text = duration["text"] as? String{
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.lbl_distance.text = text;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Inside the JSON result we are interested into the ‘overview_polyline’ which is represented in points with unknown value of “yjx..”, well it’s a polyline value. Which represented by GMSPath, then turn into GMSPolyline for displaying on the maps.
To make thing simpler, we just copy from the result of the API into our code.
// show polyline
let path = GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: "yjxP{}mkRbCr@hI|CjCp@hB^vAFnABzBG`C[ZGFXLx@wBb@_@Da@@iA@SHOZ?n@D\\J\\NTRRZRf@R")
let polyline = GMSPolyline(path:path)
polyline.strokeWidth = 4
polyline.strokeColor = UIColor.init(hue: 210, saturation: 88, brightness: 84, alpha: 1)
polyline.map = mapView

Add Delegate for More Callback
If you want to add more control like handling when the map get a tap, you can conform the GMSMapView’s delegate with the view controller.
To declare for GMSMapViewDelegate delegate.
// find where you define the GMSMapView
mapView.delegate = self
// add at the class declaration
GMSMapViewDelegate
For handling callback when you tap the maps.
// MARK:- GMSMapViewDelegate
func mapView(_ mapView: GMSMapView, didTapAt coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D) {
let marker = GMSMarker()
marker.position = coordinate
marker.title = "New Marker"
marker.map = mapView
}